Course Framework and Content
This course framework provides a description of what students should know and be able to do to qualify for college credit or placement.
The course framework includes two essential components:
1 HISTORICAL THINKING SKILLS AND REASONING PROCESSES
The historical thinking skills and reasoning processes are central to the study and practice of world history. Students should practice and develop these skills and processes on a regular basis over the span of the course.
2 COURSE CONTENT
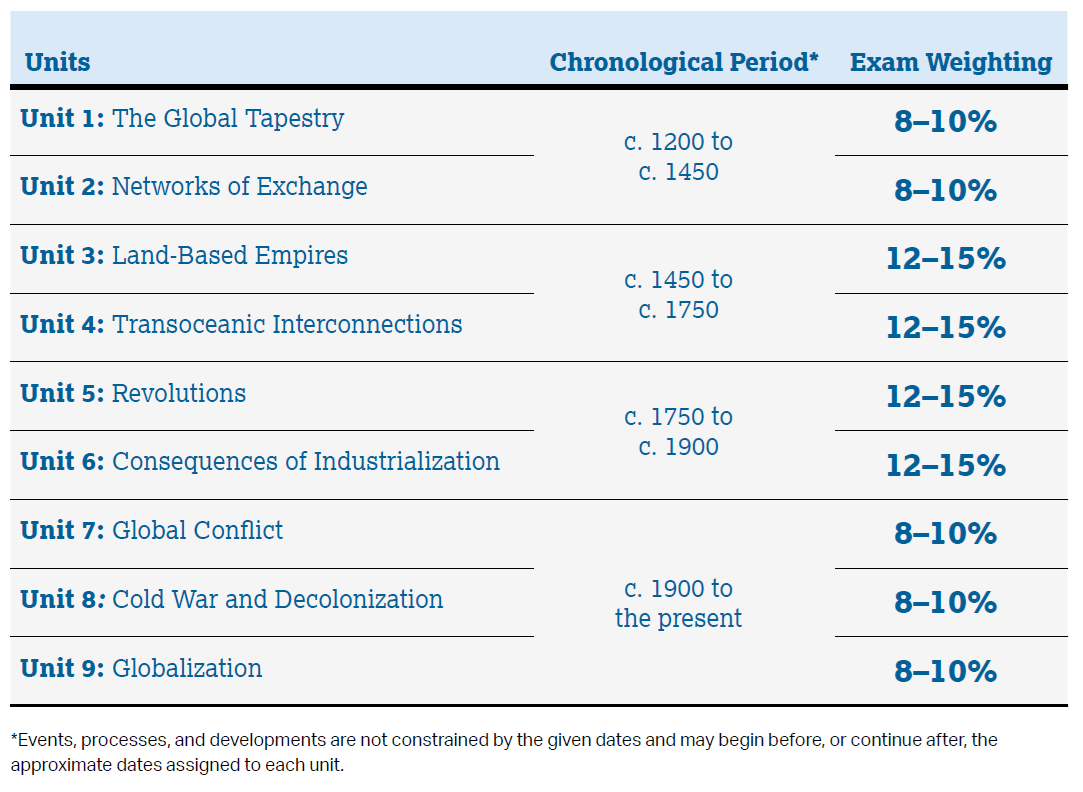
The course content is organized into commonly taught units of study that provide a suggested sequence for the course. These units comprise the content and conceptual understandings that colleges and universities typically expect students to master to qualify for college credit and/or placement. This content is grounded in themes, which are cross-cutting concepts that build conceptual understanding and spiral throughout the course.
Themes
The themes serve as the connective tissue of the course and enable students to create meaningful connections across units. They are often broader ideas that become threads that run throughout the course. Revisiting them and applying them in a variety of contexts helps students to develop deeper conceptual understanding. Below are the themes of the course and a brief description of each.
THEME 1: HUMANS AND THE ENVIRONMENT (ENV)
The environment shapes human societies, and as populations grow and change, these populations in turn shape their environments.
THEME 2: CULTURAL DEVELOPMENTS AND INTERACTIONS (CDI)
The development of ideas, beliefs, and religions illustrates how groups in society view themselves, and the interactions of societies and their beliefs often have political, social, and cultural implications.
THEME 3: GOVERNANCE (GOV)
A variety of internal and external factors contribute to state formation, expansion, and decline. Governments maintain order through a variety of administrative institutions, policies, and procedures, and governments obtain, retain, and exercise power in different ways and for different purposes.
THEME 4: ECONOMIC SYSTEMS (ECN)
As societies develop, they affect and are affected by the ways that they produce, exchange, and consume goods and services.
THEME 5: SOCIAL INTERACTIONS AND ORGANIZATION (SIO)
The process by which societies group their members and the norms that govern the interactions between these groups and between individuals influence political, economic, and cultural institutions and organization.
THEME 6: TECHNOLOGY AND INNOVATION (TEC)
Human adaptation and innovation have resulted in increased efficiency, comfort, and security, and technological advances have shaped human development and interactions with both intended and unintended consequences.
