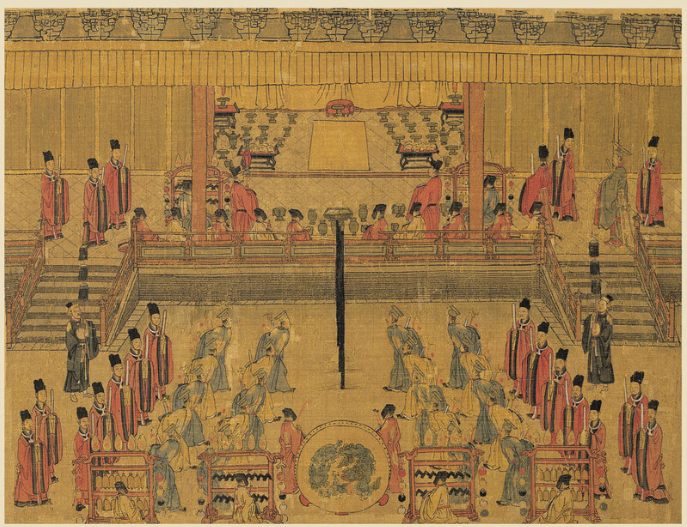
Unit 1 - Topic 1.1 The Song Dynasty
Section outline
-
c. 1200 to c. 1450
-
Learning Objective
Explain the systems of government employed by Chinese dynasties and how they developed over time.
Empires and states in Afro-Eurasia and the Americas demonstrated continuity, innovation, and diversity in the 13th century. This included the Song Dynasty of China, which utilized traditional methods of Confucianism and an imperial bureaucracy to maintain and justify its rule.
THEMATIC FOCUS - Governance GOV
A variety of internal and external factors contribute to state formation, expansion, and decline. Governments maintain order through a variety of administrative institutions, policies, and procedures, and governments obtain, retain, and exercise power in different ways and for different purposes.
Write a short reflection that answers the following question:
How did Confucian ideology both strengthen and limit the Song Dynasty’s rule? -
Turn on your VPN to watch this YouTube video about how developments in East Asia (specifically China).
-
This page contains the lecture notes.
-
Turn on your VPN to watch this YouTube video about Song Dynasty Governance.
-
Refer to this checklist for Data Based Questions.
-
Turn on your VPN to watch this YouTube video about how the Song Dynasty built their governmental system.
-
Thesis Writing Prompt
Prompt: Evaluate the extent to which the Song Dynasty represented continuity in Chinese political traditions, 1000–1300 CE. Write a 1–2 sentence thesis.
Mini-Comparison Notes (Tang vs. Song vs. Yuan Governance)
- Tang Dynasty (618–907 CE):
- Relied on Confucian ideology and the imperial exam system.
- Maintained strong military presence to secure frontiers.
- Aristocracy still influential in politics.
- Song Dynasty (960–1279 CE):
- Expanded and standardized civil service exams → larger scholar-official class.
- Stronger central bureaucracy; less power for aristocrats.
- Heavy reliance on Confucian values (Neo-Confucianism).
- Militarily weaker compared to Tang and vulnerable to invasions.
- Yuan Dynasty (1271–1368 CE):
- Mongol rulers adapted some Chinese practices but reduced role of Confucian exams (favored Mongols and Central Asians in government).
- Less reliance on scholar-officials; Confucian elite sidelined.
- Example of disruption of traditional political structures.
-
You have previously written a thesis statement. Now, we will write the complete essay. (Use your thesis statement to guide your essay.)
Prompt:
“Evaluate the extent to which the Song Dynasty represented continuity in Chinese political traditions, 1000–1300 CE.”
Essay format:
- Introduction paragraph
- hook
- general information
- thesis statement
- 2-3 body paragraphs
- topic sentence (taken from the thesis statement)
- content that supports the topic sentence
- segue - the last sentence leads to the next paragraph
- concluding paragraph
- very brief summary of the essay and a concluding paragraph
- NOTHING NEW
- Introduction paragraph
-
Watch this video to help you solve 'wordiness'.
-
Watch this video to help you write more concisely.
-
Opened: Thursday, 18 September 2025, 2:00 PMDue: Saturday, 20 September 2025, 2:30 PM
Let's rewrite our essays. Make any recommended changes, including a good introduction paragraph with a hook, general introductory information about the Song Dynasty and how they governed, and a clear conclusion paragraph.
-
Watch this video to understand more about writing a hook.
-
There are 40 questions in this practice set.
-
Opened: Monday, 22 September 2025, 8:30 AMDue: Monday, 29 December 2025, 12:56 AM
Write thesis statements for all of the following prompts:
Example:
Unit 1 – The Global Tapestry (1200–1450), Topics 1.1–1.7
Evaluate the extent to which the Song Dynasty’s reliance on Confucianism influenced Chinese political and social structures from 1200–1450. (Causation)
Thesis: The Song Dynasty’s reliance on Confucianism influenced political structures by strengthening the bureaucracy through the civil service exam and social structures by reinforcing patriarchy, although it limited innovation in some areas.Unit 1 – The Global Tapestry (1200–1450), Topics 1.1–1.7
Compare the methods of state-building used by the Abbasid Caliphate and the Delhi Sultanate during the period 1200–1450. (Comparison)
Thesis: ____________________________Unit 1 – The Global Tapestry (1200–1450), Topics 1.1–1.7
Develop an argument that evaluates how Afro-Eurasian trade networks (Silk Roads, Indian Ocean, Trans-Saharan) changed from 1200–1450. (CCOT)
Thesis: ____________________________Unit 2 – Networks of Exchange (1200–1450), Topics 2.1–2.7
Compare the effects of the Silk Roads and the Indian Ocean trade routes on the diffusion of culture in the period 1200–1450. (Comparison)
Thesis: ____________________________Unit 2 – Networks of Exchange (1200–1450), Topics 2.1–2.7
Evaluate the extent to which Mongol rule fostered cross-cultural interactions in Eurasia in the 13th and 14th centuries. (Causation)
Thesis: ____________________________Unit 3 – Land-Based Empires (1450–1750), Topics 3.1–3.8
Develop an argument that evaluates how gunpowder technology influenced state-building from 1450–1750. (CCOT)
Thesis: ____________________________Unit 3 – Land-Based Empires (1450–1750), Topics 3.1–3.8
Compare the methods of consolidating power used by the Mughal Empire and the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century. (Comparison)
Thesis: ____________________________Unit 4 – Transoceanic Interconnections (1450–1750), Topics 4.1–4.8
Evaluate the extent to which European maritime exploration transformed global trade in the period 1450–1750. (Causation)
Thesis: ____________________________Unit 4 – Transoceanic Interconnections (1450–1750), Topics 4.1–4.8
Compare the labor systems of the Spanish colonies in the Americas and the plantation economies in the Caribbean in the period 1450–1750. (Comparison)
Thesis: ____________________________Unit 5 – Revolutions (1750–1900), Topics 5.1–5.10
Evaluate the causes of the Atlantic Revolutions (American, French, Haitian, Latin American) in the period 1750–1900. (Causation)
Thesis: ____________________________Unit 5 – Revolutions (1750–1900), Topics 5.1–5.10
Develop an argument that evaluates how industrialization changed economic systems in Western Europe from 1750–1900. (CCOT)
Thesis: ____________________________Unit 6 – Consequences of Industrialization (1750–1900), Topics 6.1–6.8
Compare the responses to European imperialism in Africa and South Asia during the 19th century. (Comparison)
Thesis: ____________________________Unit 6 – Consequences of Industrialization (1750–1900), Topics 6.1–6.8
Evaluate the extent to which industrialization caused changes in global migration patterns from 1750–1900. (Causation)
Thesis: ____________________________Unit 7 – Global Conflict (1900–present), Topics 7.1–7.8
Develop an argument that evaluates how global conflict in the first half of the 20th century (World Wars I & II) changed political structures worldwide. (CCOT)
Thesis: ____________________________Unit 8 – Cold War; Decolonization (1900–present), Topics 8.1–8.9
Compare the strategies used by India and Ghana to achieve independence in the 20th century. (Comparison)
Thesis: ____________________________
-